Software Quality Control
- Ensures procedures and standards are being followed
- Software Quality Review & Inspections
- Software Quality measurements & assessments (testing)

Quality COntrol LifeCycle: V&V Perspective
Verification if the software conforms to specifications Validation if the software meets customer expectations and requirements

Reviews & Inspections
Quality management processes for written material. Applicable throughout SLC Both find anomalies/defects
Review a process/meeting where a software product's artifacts are examined by project personnel, managers, users, customers, user reps, or other interested parties for comment/approval
Inspection Disciplined engineering practice for detecting/correcting defects and preventing their leakage into field operations
Steps
- Static analysis technique
- Perform visual examination of the software product's artifacts
- Review, detect, correct: Defects, violation of design standards, other problems
Performance
Improve schedule performance

Reduce rework
- Rework accounts for 44% of development!
- Requirements = 1%
- Design = 12%
- Coding = 12%
- Testing = 19%
- Rework accounts for 44% of development!
Quality Improvement
- 60-100% of defects can be found! Reducing $$$, but have non-trivial cost (~15%)
- Pro-active tests find errors not possible through testing
- Training on the domain, corporate standards, and groups, can assess/improve quality of:
- Work/product
- Software development process
- Review process itself
Reviews
- Small changes are easier to review
- Each change should logically do ONE thing and NOT break build or tests
- Big changes should be split into series that depend on each other, and last change should turn the feature on
- Commit message should explain WHY - what is obvs from code change
Roles
- Review leader
- Reviewer
- Standards owner
- Producer
- User rep
- Recorder
- Maintenance oracle
Materials
- Source Document
- Checklist
- Supporting Documents: Invitation + master plan
- Issue/Defect Log
- Data Summary
Methods
Synchronous: Meeting based
- 5/6 Phases
- (Planning)
- Overview
- Prep
- Review/inspection
- Rework
- Follow-up
Asynchronous: Electronic based
- Formal, technical, asynchronous review method (FTArm)
- 6 Phases:
- Select Personnel and Organize Documentation
- Orientation of Participants to Assigned Task
- Private Review or Inspection
- Public Review or Inspection
- Consolidation
- Rework
- Email, char, bulletin board

Types
- Management Reviews
- Peer Reviews ask a colleague to look at it closely to identify "defects"Process:
- Author & reviewers have informational meeting on background, and distributed material
- reviewers go through material individually using a checklist as a guide
- Author collects checklists and consolidates results
- summary results presented at group meeting
- Defect based reading:
- Model possible defects in requirements docs
- For each defect class:
- Develop questions to characterize the defect class
- Characterize the scenarios: Steps to do when reviewing
- Supports reviewer's focus on specified defect classes
- Follow the scenarios and answer the questions for each

- Peer Reviews - Walk Through
- designer/programmer leads the dev team and interested parties through the software product (walk through leader, recorder, author, and team members)
- Audience makes comments & questions of possible errors, violation of standards, and other problems
- Evaluate the product's artifacts - can educate the audience
- SRS
- SDS
- Source code
- Software Test documentation
- Maintenance manual
- Release notes
- To find anomalies:improve & consider alternative implementations
- evaluate product and provide recommendations
- List of actions, due-dates, and responsible parties
- Recommendation of how to remove anomalies
- Peer Reviews - Circulation
- Artifact to be reviewed is circulated to a group of the author(s) peers for comment
- Avoids potential arguments & increases time to look at the artifact
- Removes benefits of discussion
- Peer Reviews - XP asynchronous
- Code review = small self-contained increments to understand ideas from code, and leave room to develop alternatives
- Pair Programming: helps explore terrain, on board new developers, combine complementary skills
- When there's time the whole team can review (takes time, but leaves time = parallel workflow)
- Tools(Git) can be used effectively to support the process
- You can automate things like rule checking, build/test, deployment to staging environment

- You can automate things like rule checking, build/test, deployment to staging environment
Peer Reviews - Scrum

Inspections
- Technical Reviews
- Audits
Inspections
Confirm product satisfies specs, plans/regulations, and identify differences between standard and specification. Examine source code to find anomalies/defects with/without system execution - before implementation. Cannot check non-functional quality factors (performance, usability, etc)
Roles
- Inspection leader
- Recorder
- Reader
- Author
- Inspector(s)
Materials for inspection
- SRS
- SDS
- Source code
- Software Test documentation
- Maintenance manual
- Release notes
Materials Outputted
- Project under inspection
- Inspection team members
- Inspection meeting duration
- Software product inspected
- Size of the materials inspected
- Inputs to inspection
Inspection objectives and status
- Defect list (detail)
- Defect summary list
- Disposition of the software product
- Estimate of the rework effort and completion date
Checklist
Common defects should DRIVE inspection

Values
- 30\% to 100\% net productivity increases
- 10\% - 30 \% overall project time saving
- 5-10x reduction in test execution costs & time
- Up to one order of magnitude maintenance cost reduction
- Minimal defect correction backlash during integration
- Quality improvement
Fagan's Model
- 1976, M.Fagan questioned robustness of execution based testing as a defect detection strategy
- A group reviews the artifact (requirement, design, code, etc.) for defects
- Roles verify conformace with exit criteria
- Moderator: leads inspection team
- Author (writer, analyst, designer, coder, etc): Originates/reworks document
- Reader: same as author but paraphrases/interprets doc, expressing his/her understanding (DOESN'T READ)
- Tester: Considers testability, tracability, requirements, standards, and external interactions
- Process
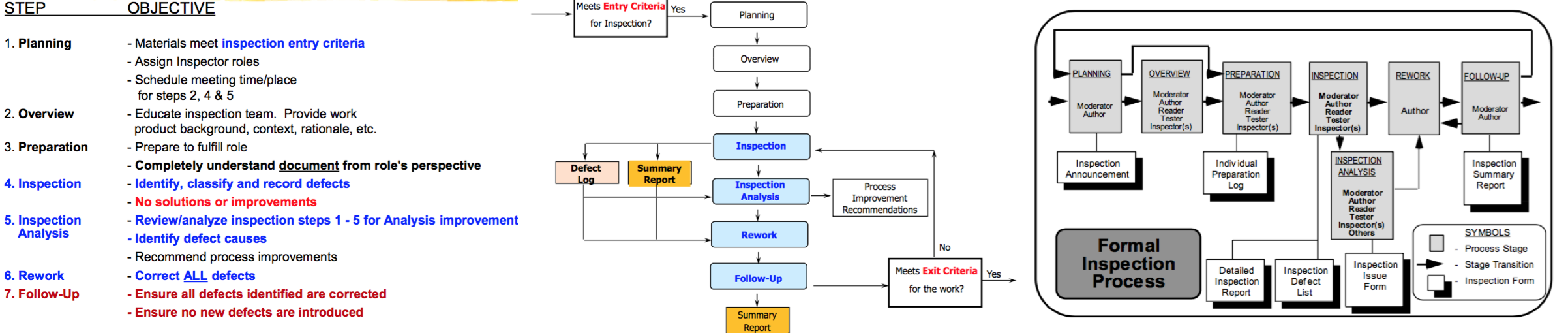
7 step inspection method process map
